Upland and Riparian Wildlife
and Habitat Survey
 Fifty-one study sites were established with remote cameras on the Keweenaw Bay Indian Reservation between January 2010 and November 2011 in upland and riparian areas. Preliminary results show that a total 23 wildlife species were detected of which 13 are considered “target” carnivore and furbearer species that were the focus of the study (black bear, raccoon, coyote, pine marten, fisher, snow shoe hare, wolf, bobcat, gray fox, red fox, weasel, otter, and badger). Two feline species, lynx and cougar were not detected during this study despite methods specific for cat species. Study sites were also surveyed for plant and habitat characteristics around each camera location. Approximately 228 plant species and 30 tree and/or shrub species were identified within the study sites during the two year study period.
Fifty-one study sites were established with remote cameras on the Keweenaw Bay Indian Reservation between January 2010 and November 2011 in upland and riparian areas. Preliminary results show that a total 23 wildlife species were detected of which 13 are considered “target” carnivore and furbearer species that were the focus of the study (black bear, raccoon, coyote, pine marten, fisher, snow shoe hare, wolf, bobcat, gray fox, red fox, weasel, otter, and badger). Two feline species, lynx and cougar were not detected during this study despite methods specific for cat species. Study sites were also surveyed for plant and habitat characteristics around each camera location. Approximately 228 plant species and 30 tree and/or shrub species were identified within the study sites during the two year study period.
Data from this study is currently being summarized and analyzed and will be combined with the wetland wildlife and habitat data. Results will be considered as we develop a KBIC Tribal Wildlife Management Plan for the KBIC L'Anse Indian Reservation. A final draft Wildlife Management Plan is scheduled to be complete and presented to KBIC Tribal Council in 2014.
Remote Camera Surveys for Carnivore and Furbearers
 The Keweenaw Bay Indian Community (KBIC) administers over 56,000 acres of land within the boundaries of the L’Anse Reservation. KBIC desires to develop a more systematic approach to management for wildlife and habitat on and near the L’Anse Reservation. A carnivore and furbearer remote camera survey was undertaken to provide baseline wildlife inventory data in which to guide the development of a Tribal Wildlife and Habitat Management Plan in 2013.
The Keweenaw Bay Indian Community (KBIC) administers over 56,000 acres of land within the boundaries of the L’Anse Reservation. KBIC desires to develop a more systematic approach to management for wildlife and habitat on and near the L’Anse Reservation. A carnivore and furbearer remote camera survey was undertaken to provide baseline wildlife inventory data in which to guide the development of a Tribal Wildlife and Habitat Management Plan in 2013.
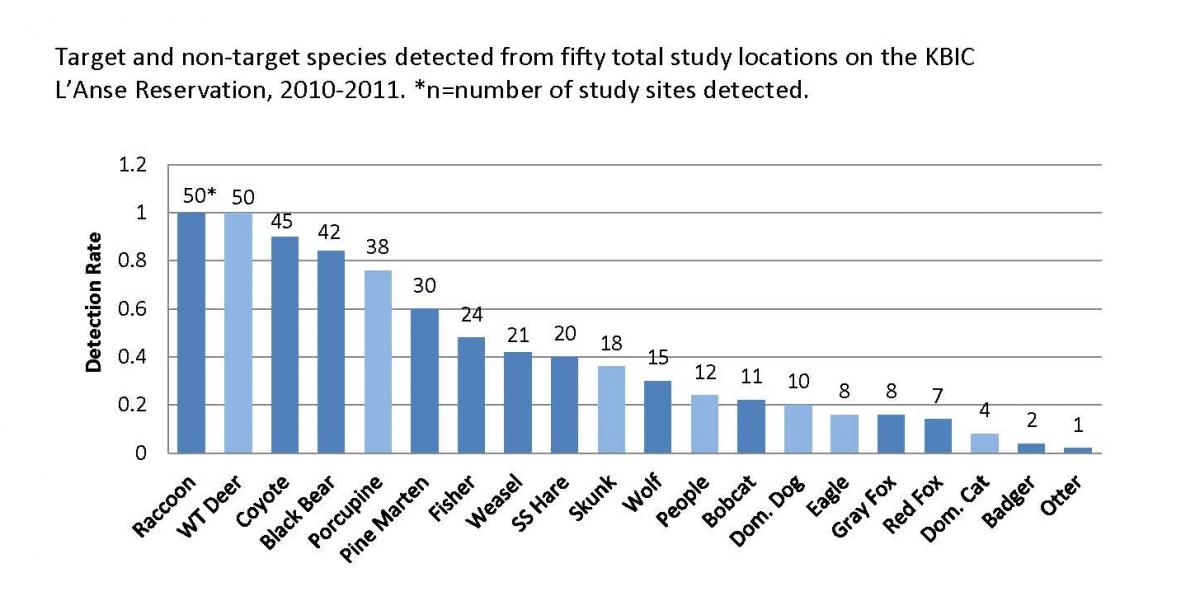
 Fifty study locations were monitored for a minimum of 30 day time periods in Winter-Spring and Summer-Fall seasons between December 2009 and September 2011. Thirteen of fifteen target species were detected and included Wolf (Canis lupus), Coyote (Canis latrans), Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes), Gray Fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), Bobcat (Lynx rufus), Black Bear (Ursus americanus), Raccoon (Procyon lotor), Weasel (Mustela spp.), Otter (Lontra canadensis), Fisher (Martes pennanti), Pine Marten (Martes americana), Badger (Taxidea taxus), and Snow Shoe Hare (Lepus americanus). Pine marten were found at more study sites (60%) than fisher (48%) however they often visited the same camera locations. Coyotes were detected at 90% of the study sites whereas wolves were found at 30%. Bobcats were detected at 22% sites, however, they did not appear to be attracted by bait but rather the scented lures which were labeled as bobcat attractants.
Fifty study locations were monitored for a minimum of 30 day time periods in Winter-Spring and Summer-Fall seasons between December 2009 and September 2011. Thirteen of fifteen target species were detected and included Wolf (Canis lupus), Coyote (Canis latrans), Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes), Gray Fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), Bobcat (Lynx rufus), Black Bear (Ursus americanus), Raccoon (Procyon lotor), Weasel (Mustela spp.), Otter (Lontra canadensis), Fisher (Martes pennanti), Pine Marten (Martes americana), Badger (Taxidea taxus), and Snow Shoe Hare (Lepus americanus). Pine marten were found at more study sites (60%) than fisher (48%) however they often visited the same camera locations. Coyotes were detected at 90% of the study sites whereas wolves were found at 30%. Bobcats were detected at 22% sites, however, they did not appear to be attracted by bait but rather the scented lures which were labeled as bobcat attractants.
|
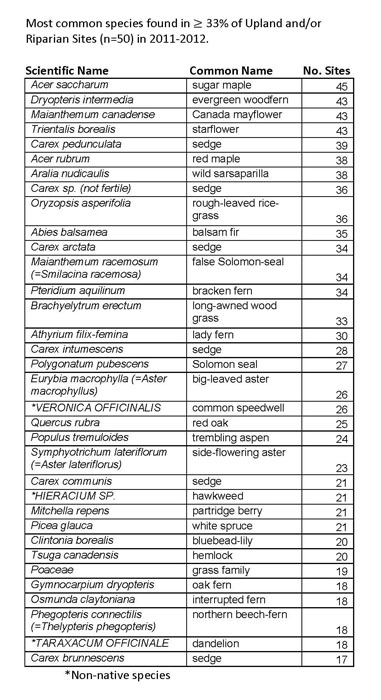
Most Common Plant Species Detected
|
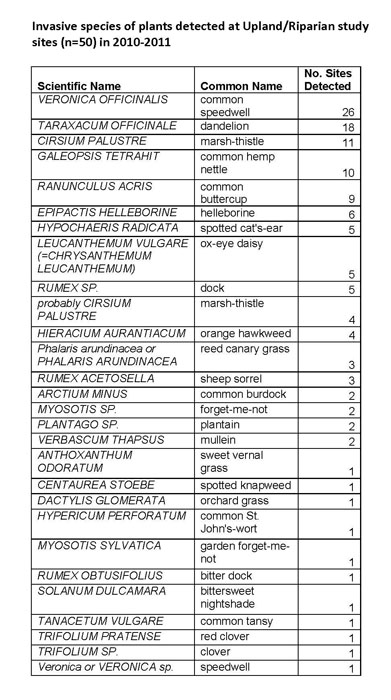
Invasive Species of Plant Detected
|
Graph of Species Detected
- List of Plant Species Detected
- Remote Camera Surveys for Carnivore and Furbearers on the KBIC L’Anse Indian Reservation
- List of plant species detected from 250 plant plots during Wildlife and Habitat surveys in 2010 and 2011
- KBIC Wildlife Inventory Results Part I
- KBIC Wildlife Inventory Results Part II